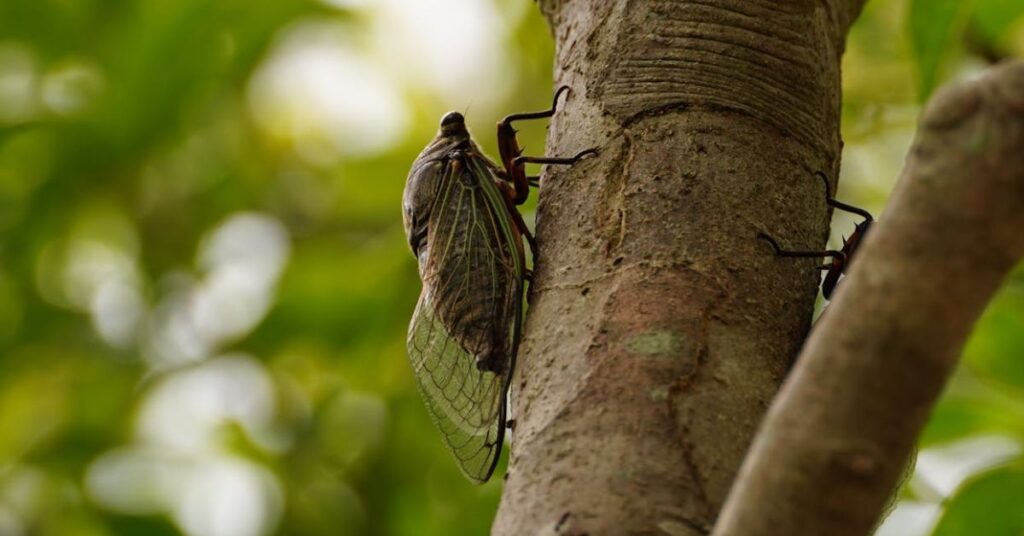
Nature is full of surprises, and 2024 is set to witness a rare and fascinating event—the doble camada de cigarras 2024 (double brood of cicadas). This unique occurrence involves the simultaneous emergence of two different broods of periodical cicadas, an event that happens only once in centuries. Millions of these noisy insects will surface, creating a spectacle that is both intriguing and significant to the environment.
In this article, we will explore what makes this event special, its impact on nature and humans, and what you should expect when these cicadas take over the outdoors.
What Causes the Doble Camada de Cigarras?
Cicadas have a unique life cycle that revolves around prolonged periods underground before emerging to reproduce. Typically, periodical cicadas appear in cycles of either 13 or 17 years. However, 2024 will witness the rare coincidence of two broods emerging at the same time: Brood XIII (17-year cicadas) and Brood XIX (13-year cicadas).
This simultaneous emergence occurs because their life cycles align once every 221 years, creating a phenomenon where an extraordinary number of cicadas take flight simultaneously.
Where Will the Doble Camada de Cigarras 2024 Occur?
The event is expected to be prominent in several regions of the United States, particularly in states that host both broods. Key areas where millions of cicadas will emerge include:
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Missouri
- Kentucky
- Tennessee
- Georgia
- North Carolina
Residents in these states should prepare for a loud and buzzing summer as these insects make their way above ground.
The Life Cycle of Periodical Cicadas
Understanding the life cycle of cicadas can help explain why this event is so rare and why it attracts so much attention.
1. Nymph Stage (Underground Life)
Cicada nymphs spend most of their lives underground, feeding on tree roots. This stage lasts for either 13 or 17 years, depending on the brood.
2. Emergence and Molting
When the soil temperature reaches about 64°F (18°C), the cicadas emerge from the ground, shed their exoskeletons, and transform into adults.
3. Mating and Singing
Male cicadas produce loud, buzzing sounds to attract females. This chorus of mating calls can reach up to 100 decibels, making it one of the loudest natural events.
4. Egg Laying and the Next Generation
After mating, females lay eggs in tree branches. The eggs hatch into tiny nymphs, which then burrow underground, restarting the cycle.
Environmental Impact of the Doble Camada de Cigarras 2024
1. Positive Effects on Ecosystems
Cicadas play an essential role in the environment. Their emergence provides food for birds, mammals, and other wildlife. Additionally, their decaying bodies enrich the soil with nutrients.
2. Potential Challenges for Trees
While cicadas do not bite or sting humans, their egg-laying behavior can cause minor damage to young trees. However, established trees typically recover without lasting effects.
3. Boost to Pollination and Soil Aeration
As cicadas emerge, they help aerate the soil, benefiting plant growth. Their presence can also enhance pollination by attracting insect-eating birds that aid in the spread of plant species.
How to Prepare for the Doble Camada de Cigarras 2024
If you live in an area affected by this event, here are a few steps to prepare:
- Protect Young Trees: Wrap small trees in netting to prevent cicadas from laying eggs in branches.
- Expect a Noisy Season: The buzzing sound will be loud, so consider noise-canceling headphones if needed.
- Secure Your Outdoor Spaces: Keep windows and doors closed to prevent cicadas from accidentally flying inside.
- Enjoy the Spectacle: This is a rare natural event, so take the opportunity to observe and appreciate its ecological significance.
Myths and Misconceptions About Cicadas
1. Cicadas Do Not Bite or Sting
Despite their loud noise and large appearance, cicadas are harmless to humans and pets.
2. They Are Not Locusts
Cicadas are often mistaken for locusts, but they do not destroy crops like locust swarms do.
3. They Are a Sign of a Healthy Environment
The presence of cicadas indicates a thriving ecosystem, as they rely on undisturbed soil and tree populations to complete their life cycle.
Conclusion:
The doble camada de cigarras 2024 is a rare and spectacular event that offers a glimpse into the incredible life cycle of cicadas. While their presence may be noisy, their impact on the environment is overwhelmingly positive. If you live in an affected area, embrace the opportunity to witness one of nature’s most fascinating occurrences, as it won’t happen again for another 221 years!
FAQs
1. How long will the cicadas stay above ground?
Once emerged, cicadas typically live for 4-6 weeks before completing their reproductive cycle and dying.
2. Are cicadas dangerous to humans or pets?
No, cicadas do not bite or sting. They are harmless and primarily a nuisance due to their loud noise.
3. Can cicadas damage crops or gardens?
Cicadas do not eat leaves or crops, but they can cause minor damage to young trees when laying eggs.
4. What is the loudest sound cicadas can produce?
Cicada mating calls can reach up to 100 decibels, similar to the noise level of a chainsaw.
5. How often does the doble camada de cigarras occur?
This event happens only once every 221 years when two broods with different cycles emerge at the same time.
6. Should I report cicada sightings?
Scientists encourage people to report sightings to help track cicada populations and study their behavior.