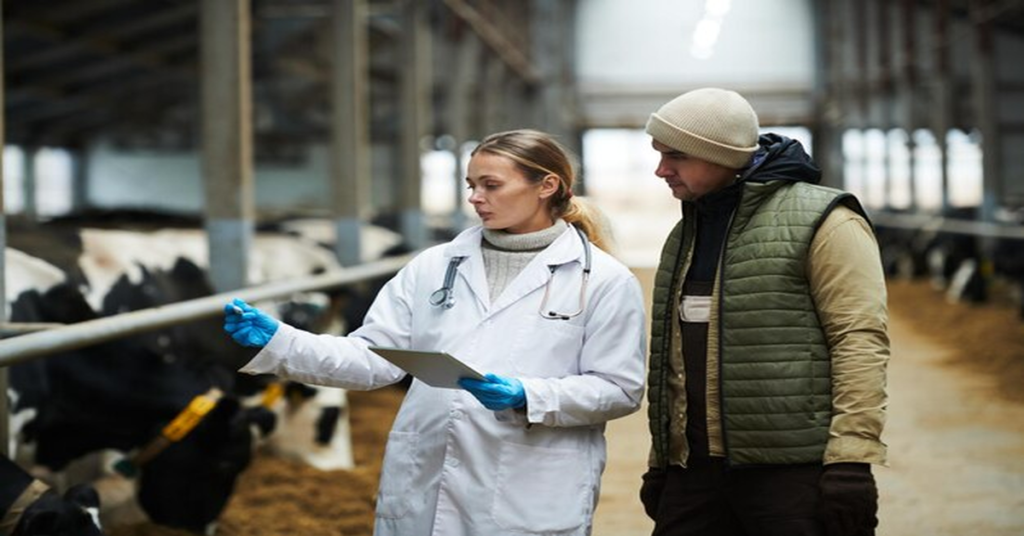
Animal Biotechnology Jobs is a dynamic and rapidly growing field that combines biology, genetics, and technology to improve animal health, productivity, and welfare. From developing genetically engineered livestock to creating vaccines and enhancing animal breeding techniques, animal biotechnology has broad applications in agriculture, medicine, and environmental conservation. As the industry expands, career opportunities in animal biotechnology are becoming more diverse and rewarding.
This article explores the different job roles in animal biotechnology, the skills required, educational pathways, career prospects, and future trends. It also provides insights into salaries, industry demands, and common job responsibilities.
Overview of Animal Biotechnology
Animal Biotechnology Jobs is the application of scientific techniques to modify animals and animal products for human benefit. This includes:
- Genetic Engineering: Modifying genes to improve disease resistance and productivity in livestock.
- Cloning: Producing genetically identical animals for research and agriculture.
- Animal Health Biotechnology: Developing vaccines and treatments for animal diseases.
- Reproductive Biotechnology: Enhancing breeding techniques through artificial insemination and embryo transfer.
- Nutrigenomics: Studying how nutrition affects gene expression in animals.
- Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Using animals to produce biologically active substances for medical applications.
These advancements are revolutionizing agriculture, medicine, and conservation, creating numerous career opportunities for biotechnology professionals.
Career Opportunities in Animal Biotechnology
1. Animal Geneticist
Animal geneticists study genes to improve breeding programs, enhance disease resistance, and increase productivity in livestock. Responsibilities include:
- Conducting research on genetic traits and heredity.
- Developing genetically modified animals with desirable characteristics.
- Analyzing DNA to prevent genetic disorders.
2. Veterinary Biotechnologist
Veterinary biotechnologists work on disease prevention and treatment in animals. They develop vaccines, diagnostics, and therapeutic solutions for livestock and pets. Key duties include:
- Researching animal diseases and developing treatments.
- Creating genetically engineered vaccines.
- Collaborating with veterinarians and pharmaceutical companies.
3. Animal Cloning Specialist
Cloning specialists focus on reproductive biotechnology, producing genetically identical animals for research and breeding programs. Job tasks involve:
- Performing somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT).
- Conducting experiments to improve cloning efficiency.
- Ensuring ethical and regulatory compliance.
4. Livestock Biotechnology Specialist
These professionals work to enhance livestock health, productivity, and sustainability through biotechnology. Responsibilities include:
- Developing genetically superior livestock breeds.
- Improving feed efficiency through genetic modification.
- Reducing environmental impact by optimizing animal production.
5. Wildlife Biotechnologist
Wildlife biotechnologists use genetic tools to conserve endangered species and restore biodiversity. Duties involve:
- Conducting DNA analysis of wildlife populations.
- Developing conservation strategies for endangered species.
- Assisting in wildlife rehabilitation projects.
6. Research Scientist in Animal Biotechnology
Research scientists contribute to scientific knowledge by conducting studies on animal genetics, cloning, and health. Responsibilities include:
- Designing and executing experiments.
- Publishing research findings in scientific journals.
- Securing funding for biotechnology projects.
7. Bioinformatics Specialist in Animal Science
Bioinformatics specialists analyze genetic data to optimize breeding programs and animal health initiatives. They work on:
- Developing algorithms to analyze genetic sequences.
- Identifying genetic markers for disease resistance.
- Assisting in genome mapping projects.
8. Animal Biopharmaceutical Scientist
Animal biopharmaceutical scientists develop biopharmaceuticals derived from animal cells, including:
- Producing therapeutic proteins using transgenic animals.
- Researching monoclonal antibodies for veterinary applications.
- Ensuring regulatory compliance for biologics.
Educational Pathways and Skills Required
1. Educational Requirements
To enter the field of animal biotechnology, a degree in biotechnology, animal science, genetics, veterinary medicine, or a related field is required. Typical academic paths include:
- Bachelor’s Degree: Animal Biotechnology, Veterinary Science, Genetics, or Biotechnology.
- Master’s Degree: Specialization in animal genetics, molecular biology, or bioinformatics.
- Ph.D.: Required for research, academia, and advanced scientific roles.
2. Essential Skills
- Molecular Biology Techniques: PCR, gene sequencing, and genetic engineering.
- Data Analysis & Bioinformatics: Interpreting genetic data and statistical modeling.
- Animal Husbandry Knowledge: Understanding livestock management and breeding.
- Laboratory Skills: Working with cell cultures, cloning, and genetic modification.
- Regulatory Compliance: Knowledge of ethical guidelines and biosafety regulations.
Industry Demand and Salary Outlook
Animal biotechnology careers offer competitive salaries and job stability due to the growing demand for animal health solutions.
1. Salary Range
- Entry-Level Positions: $50,000 – $70,000 per year.
- Mid-Level Scientists: $75,000 – $100,000 per year.
- Senior Researchers and Specialists: $100,000+ per year.
- Industry Executives and Consultants: $120,000+ per year.
2. Job Market Trends
- Increasing demand for genetically improved livestock.
- Growth in veterinary biotechnology and animal pharmaceuticals.
- Rising use of bioinformatics in animal genetics.
- Expansion of conservation biotechnology for endangered species.
Future Trends in Animal Biotechnology Careers
1. Gene Editing with CRISPR
CRISPR technology is transforming animal biotechnology by enabling precise genetic modifications to enhance disease resistance and productivity.
2. Alternative Protein Production
Biotechnology is being used to develop lab-grown meat and alternative protein sources, reducing environmental impact.
3. AI and Big Data in Animal Science
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are optimizing breeding programs and disease monitoring in livestock.
4. Personalized Veterinary Medicine
Advances in genomics allow for personalized treatment plans tailored to individual animals.
5. Sustainable Livestock Farming
Biotechnology is helping develop eco-friendly livestock management practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Animal biotechnology is an exciting field with diverse career opportunities ranging from genetic research and vaccine development to conservation science and bioinformatics. As the industry continues to expand, the demand for skilled professionals will only grow. A career in animal biotechnology offers not only financial rewards but also the satisfaction of contributing to scientific advancements that improve animal health, agriculture, and environmental sustainability.
FAQs
1. What degree do I need for a career in animal biotechnology?
A bachelor’s degree in biotechnology, animal science, genetics, or veterinary medicine is required, with advanced roles requiring a master’s or Ph.D.
2. What are the highest-paying jobs in animal biotechnology?
Senior research scientists, animal biopharmaceutical scientists, and biotechnology executives are among the highest-paid professionals in this field.
3. Are there job opportunities for animal biotechnologists in conservation?
Yes, wildlife biotechnologists use genetic research to conserve endangered species and restore ecosystems.
4. What industries hire animal biotechnology professionals?
Industries include agriculture, pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicine, genetic research, and environmental conservation.
5. What skills are essential for success in animal biotechnology careers?
Key skills include molecular biology, bioinformatics, genetic engineering, regulatory compliance, and laboratory techniques.
6. What is the future of animal biotechnology jobs?
The future is promising, with advancements in gene editing, AI-driven breeding programs, and sustainable livestock farming creating new career opportunities.
This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into the diverse career options available in animal biotechnology, helping aspiring professionals navigate their career paths in this innovative industry.