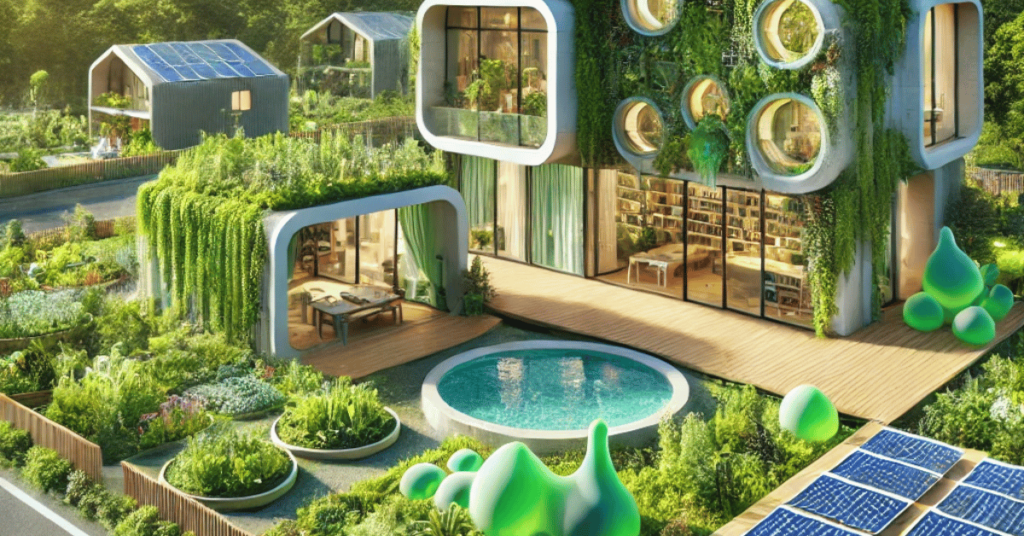
In an age where sustainability and innovation are crucial for addressing global challenges, Casa Amiba emerges as a beacon of eco-friendly architectural excellence. A harmonious blend of nature and technology, Casa Amiba’s represents a new paradigm in sustainable living. This article explores Casa Amiba’s in detail, highlighting its origin, principles, design features, environmental benefits, challenges, and future potential.
What is Casa Amiba?
Casa Amiba’s, translated as “House Amoeba,” takes inspiration from the natural world, particularly the adaptable and efficient design of amoebas. It is an architectural concept and a lifestyle philosophy that emphasizes modularity, adaptability, and sustainability. Casa Amiba’s incorporates cutting-edge technology and eco-friendly practices to minimize environmental impact while maximizing functionality and comfort.
The Vision Behind Casa Amiba
The idea of Casa Amiba’s was conceived to address the urgent need for sustainable housing solutions. With urbanization, climate change, and resource depletion posing significant challenges, Casa Amiba’s aims to:
- Reduce Carbon Footprint: Promote energy-efficient construction and renewable energy integration.
- Enhance Adaptability: Create homes that adapt to changing needs and environments.
- Encourage Community Living: Foster interconnected, sustainable communities.
- Preserve Natural Resources: Employ materials and methods that conserve water, energy, and other resources.
Core Principles of Casa Amiba
Casa Amiba’s design philosophy is rooted in five fundamental principles:
- Biomimicry: Drawing inspiration from nature’s efficiency and resilience.
- Sustainability: Prioritizing renewable materials and energy sources.
- Adaptability: Modular structures that can evolve with occupants’ needs.
- Energy Efficiency: Integration of passive design elements and renewable energy systems.
- Circular Economy: Encouraging recycling, upcycling, and minimal waste generation.
Design Features of Casa Amiba
1. Modular Architecture
Casa Amiba’s employs modular construction techniques, allowing homes to be assembled, disassembled, and expanded with ease. This adaptability ensures:
- Quick construction.
- Cost efficiency.
- Scalability for different family sizes or uses.
2. Eco-Friendly Materials
Sustainable materials such as bamboo, recycled steel, and rammed earth are central to Casa Amiba’s construction. These materials are:
- Renewable and biodegradable.
- Locally sourced to reduce transportation emissions.
- Durable, ensuring long-lasting structures.
3. Passive Design
Casa Amiba’s integrates passive design strategies to reduce energy consumption, including:
- Natural Ventilation: Cross-ventilation techniques minimize reliance on artificial cooling.
- Solar Orientation: Maximizing sunlight exposure for warmth and energy generation.
- Thermal Insulation: Maintaining consistent indoor temperatures year-round.
4. Renewable Energy Systems
A hallmark of Casa Amiba’s is its commitment to renewable energy. Solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems power the homes, ensuring minimal reliance on non-renewable resources.
5. Smart Home Technology
The integration of IoT devices enhances Casa Amiba’s functionality. Features include:
- Energy monitoring systems.
- Automated lighting and temperature controls.
- Water management systems to track and optimize usage.
6. Green Spaces
Incorporating vegetation into the design is a priority. Rooftop gardens, vertical green walls, and communal green spaces:
- Improve air quality.
- Reduce urban heat island effects.
- Promote mental well-being.
Environmental Benefits of Casa Amiba
1. Reduced Energy Consumption
By utilizing passive design and renewable energy systems, Casa Amiba’s significantly lowers energy usage, resulting in:
- Decreased greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lower utility bills for occupants.
2. Water Conservation
Casa Amiba’s employs water-saving technologies such as:
- Rainwater harvesting systems.
- Greywater recycling.
- Low-flow fixtures to minimize water wastage.
3. Waste Reduction
The emphasis on modularity and recyclable materials ensures minimal construction and operational waste. Additionally, composting systems manage organic waste effectively.
4. Biodiversity Promotion
The inclusion of green spaces fosters local biodiversity, creating habitats for plants, birds, and insects.
5. Climate Resilience
Casa Amiba’s design prioritizes resilience to natural disasters such as floods, heatwaves, and earthquakes, ensuring longevity and safety.
Applications of Casa Amiba
1. Urban Housing
In densely populated cities, Casa Amiba’s serves as a sustainable alternative to traditional apartment complexes. Modular units can be stacked vertically to optimize land use.
2. Disaster Relief Housing
Casa Amiba’s quick assembly and resilience make it ideal for temporary housing in disaster-stricken areas.
3. Remote Eco-Lodges
Tourism ventures in remote areas benefit from Casa Amiba’s low-impact, eco-friendly design.
4. Educational Institutions
Sustainable dormitories and classrooms based on Casa Amiba’s principles enhance learning environments while reducing operational costs.
5. Community Living
Eco-villages centered around Casa Amiba’s promote sustainable lifestyles and shared resources.
Challenges and Limitations
While Casa Amiba presents numerous advantages, it also faces challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Sustainable materials and renewable energy systems can be expensive upfront.
- Regulatory Barriers: Building codes and zoning laws may not always accommodate innovative designs.
- Maintenance Needs: Advanced systems such as IoT devices and renewable energy setups require specialized upkeep.
- Awareness and Acceptance: Convincing communities and stakeholders to adopt Casa Amiba’s can be a hurdle.
- Supply Chain Issues: Accessing sustainable materials locally may pose logistical challenges.
Future Potential of Casa Amiba
Casa Amiba’s has immense potential to revolutionize the construction and housing industries. Future developments include:
- Enhanced Energy Storage: Integrating advanced battery systems for greater energy autonomy.
- AI Integration: Employing AI for predictive maintenance and optimized resource management.
- Mass Customization: Leveraging 3D printing to tailor modular units to individual preferences.
- Policy Advocacy: Collaborating with governments to create supportive frameworks for sustainable housing.
- Global Expansion: Adapting Casa Amiba’s to diverse climates and cultural contexts worldwide.
Conclusion
Casa Amiba’s is more than a building concept; it is a vision for a sustainable future. By prioritizing adaptability, eco-friendliness, and technological integration, Casa Amiba’s offers a viable solution to the housing and environmental challenges of the 21st century. However, realizing its full potential requires collective effort from policymakers, architects, and communities.
FAQs About Casa Amiba
1. What is Casa Amiba? Casa Amiba’s is an innovative architectural concept focusing on sustainable living, modular design, and environmental conservation.
2. What materials are used in Casa Amiba? Casa Amiba’s utilizes eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, recycled steel, rammed earth, and other sustainable resources.
3. How does Casa Amiba promote sustainability? Casa Amiba’s incorporates renewable energy, water-saving technologies, waste reduction practices, and green spaces to minimize environmental impact.
4. Where can Casa Amiba be applied? Applications include urban housing, disaster relief housing, eco-lodges, educational institutions, and community living projects.
5. What are the challenges of implementing Casa Amiba? Challenges include high initial costs, regulatory barriers, maintenance needs, and awareness issues.
6. What is the future of Casa Amiba? The future includes advancements in energy storage, AI integration, mass customization, supportive policies, and global adaptability.