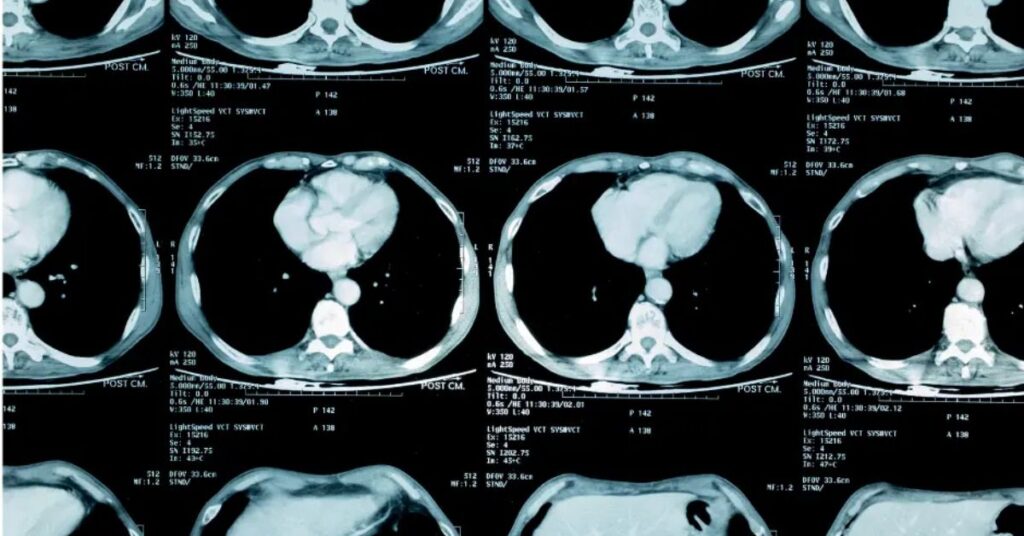
Have you or someone you know recently undergone a lung screening and received an LRADS classification? If so, you might be wondering about the next steps in monitoring lung nodules. The LRADS follow-up is crucial for assessing and managing lung nodules detected during imaging studies, particularly in patients at risk for lung cancer. In this article, we will explore what LRADS is, the significance of follow-up evaluations, and how to navigate the management process effectively.
What is LRADS?
LRADS, or Lung-RADS (Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System), is a standardized reporting system developed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) for evaluating lung nodules identified on low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans. This system categorizes nodules based on their size, appearance, and characteristics to aid radiologists in determining the appropriate follow-up actions.
- Categories of LRADS: The LRADS system classifies nodules into several categories, ranging from LRADS 1 (negative) to LRADS 4 (suspicious for malignancy). Each category has specific follow-up recommendations to ensure appropriate monitoring.
- Purpose: The primary purpose of LRADS is to improve the accuracy and consistency of reporting lung nodules, ultimately facilitating better patient management and outcomes.
Why is LRADS Follow-Up Important?
Following the initial identification of lung nodules, LRADS follow-up plays a critical role in patient care for several reasons:
- Early Detection of Cancer: Timely follow-up evaluations are essential for detecting any changes in nodules that could indicate malignancy. Early detection significantly improves treatment options and patient prognosis.
- Reducing Anxiety: Knowing that there is a structured follow-up plan can help alleviate the anxiety that often accompanies the discovery of lung nodules. Patients can feel more in control of their health outcomes when they understand the next steps.
- Tailored Management: Different categories of LRADS require different management strategies. Follow-up evaluations allow healthcare providers to tailor their approach based on the risk associated with the specific nodule.
Understanding the LRADS Follow-Up Process
The follow-up process after an LRADS classification involves several steps, each designed to ensure comprehensive evaluation and management of lung nodules.
1. Initial Assessment and Classification
Upon receiving imaging results, the radiologist will classify the lung nodules according to the LRADS system. This classification is critical in determining the follow-up actions required. For example:
- LRADS 1: No nodules or nodules that are not clinically significant may require no follow-up.
- LRADS 2: Benign nodules that typically require routine follow-up after a certain period.
- LRADS 3: Indeterminate nodules warrant closer monitoring with follow-up imaging.
- LRADS 4: Suspicious nodules necessitate further investigation, including possible biopsy.
2. Developing a Follow-Up Plan
Based on the LRADS classification, the healthcare team will develop a personalized follow-up plan. This plan may include:
- Scheduled Imaging: For LRADS 2 and 3 nodules, follow-up imaging may be scheduled at regular intervals, such as 6 months, 1 year, or 2 years, to monitor for any changes in size or appearance.
- Referral to Specialists: In cases of LRADS 4 or if there is a significant concern, patients may be referred to a pulmonologist or oncologist for further evaluation and management.
- Patient Education: It’s important for patients to understand the implications of their LRADS classification and the importance of adhering to the follow-up plan. This can empower them to take an active role in their healthcare.
3. Follow-Up Imaging
Follow-up imaging is a critical component of the LRADS follow-up process. Depending on the initial classification, patients may undergo various imaging studies:
- Low-Dose CT Scans: These scans are often used for follow-up assessments as they minimize radiation exposure while providing detailed images of the lungs.
- Comparison with Previous Images: Radiologists will compare follow-up images with previous scans to assess for any changes in the size or characteristics of the nodules.
4. Interpretation of Results
After follow-up imaging, the results will be interpreted by the radiologist. This interpretation is vital for determining the next steps in management:
- Stable Nodules: If the nodules remain stable over time (no significant change in size or characteristics), they may continue to be monitored with routine follow-up as recommended.
- Changes Observed: If there are any changes, such as an increase in size or alterations in shape, further evaluation may be necessary, including possible biopsy or other diagnostic procedures.
Risk Factors for Lung Nodules
Understanding the risk factors associated with lung nodules can provide context for the LRADS follow-up process. Common risk factors include:
- Smoking History: Individuals with a history of smoking are at a higher risk for developing lung cancer, making follow-up evaluations even more critical.
- Age: The risk of lung cancer increases with age, particularly in individuals over 50.
- Family History: A family history of lung cancer can also increase an individual’s risk.
- Previous Lung Conditions: Patients with a history of lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary fibrosis, may be at an increased risk for lung nodules.
Best Practices for LRADS Follow-Up
To ensure effective management of lung nodules, patients and healthcare providers can follow best practices during the LRADS follow-up process:
- Adhere to Follow-Up Recommendations: Patients should closely follow the follow-up plan established by their healthcare provider, attending all scheduled imaging appointments.
- Communicate with Healthcare Providers: Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential. Patients should report any new symptoms, such as persistent cough, chest pain, or unexplained weight loss, as these may warrant further evaluation.
- Stay Informed: Patients should educate themselves about their condition, understand their LRADS classification, and ask questions about their follow-up plan.
- Consider a Second Opinion: If there are any uncertainties regarding the follow-up plan or the classification, patients may seek a second opinion from another healthcare provider or specialist.
The Role of Technology in LRADS Follow-Up
Advancements in technology are significantly enhancing the effectiveness of the LRADS follow-up process. Here are a few ways technology is improving patient management:
- Telemedicine: Remote consultations and follow-up appointments can help ensure that patients have access to healthcare professionals without the need for travel. This convenience encourages adherence to follow-up plans.
- AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence is increasingly being used to analyze imaging studies, helping radiologists identify subtle changes in nodules that may require closer monitoring.
- Patient Portals: Many healthcare providers offer online patient portals where individuals can access their medical records, imaging results, and follow-up schedules. This transparency promotes patient engagement and adherence to follow-up care.
Challenges in LRADS Follow-Up
While the LRADS follow-up process is essential, it is not without challenges. Some of the common hurdles include:
- Patient Adherence: Some patients may struggle to adhere to follow-up recommendations due to various factors, such as anxiety, misunderstanding of the importance, or logistical challenges in scheduling appointments.
- Access to Care: Patients in underserved areas may face difficulties accessing specialized care, making it challenging to receive timely follow-up evaluations.
- Variability in Practice: Differences in healthcare practices and adherence to guidelines can lead to inconsistencies in follow-up care across various providers.
Conclusion:
The LRADS follow-up process is a critical component in the management of lung nodules, providing a structured approach to monitor potential malignancies. Early detection and timely follow-up evaluations can significantly enhance patient outcomes, ultimately reducing anxiety and improving quality of life. By understanding the importance of LRADS and adhering to follow-up recommendations, patients can play an active role in their healthcare journey.
Whether you are a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, being informed about the LRADS follow-up process can empower better decision-making and promote a proactive approach to lung health.