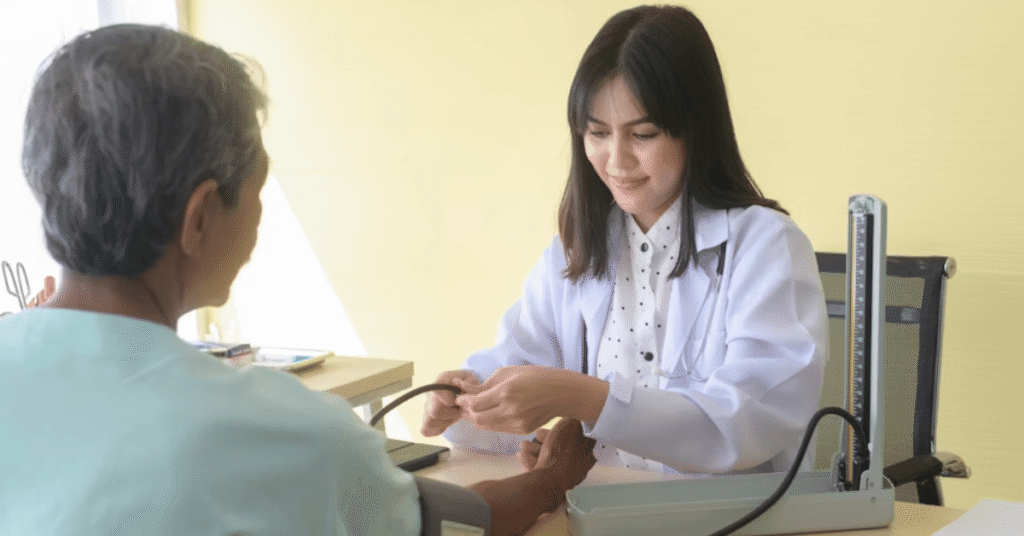
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) doctors specialize in diagnosing and treating disorders that affect the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. For anyone suffering from jaw pain, clicking sounds, headaches, or difficulty chewing, visiting a TMJ doctor can be a transformative step toward relief. The temporomandibular joint connects the jawbone to the skull, and when this connection becomes strained or misaligned, it leads to a condition known as TMJ disorder. TMJ doctors, often oral and maxillofacial specialists, bring together medical science, dental precision, and musculoskeletal expertise to treat these complex issues. Understanding who these doctors are, what they do, and how they help is crucial for patients seeking lasting comfort and improved oral function.
TMJ disorders are more common than most people realize, affecting millions globally, yet many cases go undiagnosed. The best TMJ doctors don’t merely treat symptoms; they investigate underlying causes such as stress, teeth grinding, posture, or joint misalignment. This article explores their roles, treatment techniques, and the advanced technologies that shape modern TMJ care. It also highlights the patient journey—from initial consultation to full recovery—making this guide a complete resource for those searching for trustworthy, detailed, and new insights about TMJ doctors and their practice in the modern medical landscape.
What Does a TMJ Doctor Do?
A TMJ doctor specializes in understanding the mechanics of the jaw joint, the muscles that control it, and how both interact with the skull. Their work involves diagnosing issues like jaw stiffness, facial pain, and chronic migraines linked to jaw misalignment. Many TMJ doctors come from dental, orthopedic, or maxillofacial backgrounds, combining their knowledge of bone structures and oral anatomy to offer comprehensive care. These specialists use physical examinations, imaging studies, and patient histories to identify the root cause of discomfort.
TMJ doctors focus on restoring normal joint movement and reducing muscle tension. They often start with conservative treatments such as bite guards, physical therapy, or anti-inflammatory medication before considering surgical solutions. Their goal is to help patients regain the ability to speak, eat, and smile without pain or restriction. As Dr. Martin Langley, a maxillofacial expert, once said, “TMJ treatment is not about fixing a joint—it’s about restoring balance to the entire facial system.” This philosophy defines their multidisciplinary approach, ensuring that no symptom is treated in isolation.
The Evolution of TMJ Treatments
Decades ago, TMJ disorders were poorly understood, and treatments were largely experimental. Today, the field has evolved into a highly specialized branch of medicine. TMJ doctors now integrate technologies such as 3D imaging, digital bite analysis, and minimally invasive procedures to provide targeted care. What was once treated as a simple dental issue is now recognized as a complex interplay of muscles, nerves, and skeletal alignment.
Modern TMJ doctors prioritize personalized treatment plans. They consider lifestyle factors, such as stress levels and sleep quality, alongside physical assessments. Some use advanced therapies like ultrasound-guided injections or laser-assisted muscle relaxation to promote healing. The evolution also reflects a shift in patient awareness; people now seek non-surgical options and preventive strategies. “Pain in the jaw is often the body’s way of signaling imbalance,” notes Dr. Evelyn Moore, a leading TMJ specialist. “By listening to that signal, we can correct not just the pain, but the cause.”
Common Causes of TMJ Disorders
TMJ disorders can arise from a variety of sources, making diagnosis challenging. One of the leading causes is bruxism, or teeth grinding, which puts excess pressure on the jaw joint. Poor posture, especially forward head posture from extended screen time, can also strain the joint’s alignment. Stress plays a major role, as clenching the jaw under tension tightens the facial muscles and exacerbates joint inflammation.
Additionally, trauma to the jaw or arthritis within the joint can contribute to chronic dysfunction. TMJ doctors examine these causes through detailed consultation and imaging tests. They emphasize that early detection is crucial—addressing minor symptoms before they escalate into severe, chronic pain. By understanding the patient’s habits, physical condition, and stress factors, TMJ doctors create a holistic roadmap to recovery. The diversity of causes underlines why treatment cannot rely on a single approach but must blend medicine, therapy, and patient education.
Diagnostic Process in TMJ Care
TMJ doctors follow a systematic diagnostic process to ensure accurate identification of the disorder. The first step involves a detailed patient history, where symptoms such as jaw clicking, locking, or headaches are noted. Physical examination comes next, during which the doctor palpates the jaw muscles and observes jaw movement patterns. Advanced imaging tools, including panoramic X-rays, CT scans, and MRI, provide detailed insights into joint anatomy and potential tissue damage.
TMJ specialists also use occlusal analysis—evaluating how teeth come together when the mouth closes—to detect bite imbalances that may contribute to jaw pain. The diagnostic process is crucial, as TMJ symptoms can mimic other conditions like ear infections or neuralgia. A misdiagnosis may lead to ineffective treatment or unnecessary surgery. Therefore, TMJ doctors invest significant time in confirming the true source of discomfort. This precision is what sets specialized TMJ care apart from general dental or medical consultation.
Table 1: Common Diagnostic Tools Used by TMJ Doctors
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Assess muscle tension and jaw movement | Detects pain areas and motion limitations |
| MRI Scan | Evaluate joint tissues | Identifies disc displacement or inflammation |
| CT Scan | View bone structure | Reveals structural abnormalities or fractures |
| Occlusal Analysis | Study bite alignment | Determines if teeth position affects joint function |
| Patient History | Collect symptom data | Links lifestyle habits to jaw dysfunction |
Non-Surgical Treatments Offered by TMJ Doctors
TMJ doctors often begin with non-invasive therapies designed to ease pain and restore function. The most common approach involves oral splints or night guards, which prevent teeth grinding and reduce strain. Physical therapy helps strengthen jaw muscles and improve mobility. Doctors may also recommend stress management exercises, as emotional tension often intensifies jaw clenching.
In cases of inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections are prescribed. Ultrasound therapy and cold laser treatments are modern techniques that encourage healing and reduce swelling. Dietary adjustments, such as eating soft foods and avoiding excessive chewing, support recovery. These non-surgical options represent the foundation of TMJ care, offering relief for most patients without the need for invasive procedures. They also align with the broader medical trend of personalized, patient-centered care—addressing not just the pain, but the habits that cause it.
Surgical Options and Advanced Interventions
When conservative methods fail, TMJ doctors may consider surgical procedures. Arthrocentesis, a minimally invasive technique, flushes out debris and lubricates the joint, reducing inflammation. Arthroscopy allows surgeons to view the joint interior and make precise corrections. Open-joint surgery, while rare, becomes necessary when structural deformities are severe or joint replacement is required.
These surgeries are performed under careful diagnostic guidance to ensure precision and minimal recovery time. Post-surgical rehabilitation focuses on physical therapy and jaw exercises to restore mobility. TMJ doctors emphasize that surgery is a last resort, not a first-line solution. With modern advancements, even surgical cases are now less invasive, reducing hospital stays and improving recovery rates. Dr. Helen Ruiz, a craniofacial surgeon, explains, “In TMJ surgery, success is not measured by incision size but by the restoration of pain-free motion.”
Patient Journey: From Pain to Recovery
The patient journey under a TMJ doctor’s care involves multiple stages. It begins with consultation and diagnosis, followed by a tailored treatment plan. Patients usually undergo a mix of physical therapy, splint therapy, and behavioral modifications over several months. Follow-up appointments monitor progress, allowing the doctor to make necessary adjustments.
Psychological support is often integrated, as chronic jaw pain can lead to anxiety or depression. Patients are taught jaw relaxation techniques, posture correction, and self-care routines. Recovery timelines vary—from weeks for mild cases to months for chronic conditions. However, the long-term outcomes are generally positive, with most patients reporting significant improvement in comfort and function. This comprehensive, step-by-step approach is what defines the excellence of TMJ doctors in modern medicine.
Table 2: Typical TMJ Treatment Timeline
| Treatment Stage | Duration | Focus Area | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Diagnosis | 1–2 weeks | Symptom assessment | Confirm TMJ disorder |
| Conservative Therapy | 4–12 weeks | Pain management | Reduced inflammation |
| Physical Therapy | Ongoing | Jaw mobility | Improved function |
| Surgical Option (if needed) | Variable | Structural correction | Long-term stability |
| Maintenance & Follow-Up | Continuous | Prevention | Recurrence control |
Lifestyle and Home Care Recommendations
TMJ doctors frequently guide patients on lifestyle habits that can prevent symptom recurrence. Simple measures like avoiding hard foods, chewing gum, or excessive jaw movement can significantly reduce strain. Applying warm compresses relaxes tight muscles, while posture correction helps maintain proper alignment. Stress management through yoga or meditation also aids recovery.
Doctors may recommend exercises like gentle jaw stretching and controlled mouth opening to maintain flexibility. Sleep posture matters too—patients are advised to sleep on their back rather than their side. These home-based practices, when combined with professional care, create sustainable results. TMJ doctors believe that lasting relief depends not only on clinical treatment but also on patient awareness and consistent self-care.
The Future of TMJ Medicine
As technology advances, TMJ doctors are integrating digital diagnostics and AI-based imaging into their practice. These tools can predict joint wear, simulate jaw motion, and personalize treatment plans with remarkable accuracy. Telehealth consultations are also growing, allowing patients in remote areas to access expert advice. The future of TMJ medicine lies in precision diagnostics, minimally invasive interventions, and holistic rehabilitation.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaboration—between dentists, neurologists, and physiotherapists—is becoming standard. This team-based model ensures that every aspect of a patient’s condition is addressed. As Dr. Lauren Patel remarks, “The next decade of TMJ care will be defined by intelligence—both human and digital.” This forward-looking approach promises a new era of comfort and accessibility for patients worldwide.
Conclusion
TMJ doctors occupy a crucial role in modern healthcare, addressing a condition that affects millions yet remains underdiagnosed. Their approach combines medical science, patient education, and evolving technology to restore both comfort and confidence. Through personalized care, these specialists not only treat pain but also uncover the hidden factors—stress, posture, or lifestyle—that cause it.
Their growing field reflects a shift toward patient-centered medicine, where every diagnosis considers the person, not just the symptom. For anyone experiencing persistent jaw discomfort, seeking a TMJ doctor can mark the beginning of real relief. As awareness grows and innovation continues, TMJ doctors remain at the forefront of restoring one of the most essential human functions—the ability to speak, eat, and live without pain.
FAQs
1. What type of doctor should I see for TMJ pain?
You should consult a TMJ specialist, often an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, dentist with TMJ training, or a craniofacial pain expert. These professionals have specialized knowledge in diagnosing and treating temporomandibular joint disorders.
2. Can TMJ disorders go away without treatment?
Mild TMJ issues can improve with rest, posture correction, and lifestyle changes. However, chronic or severe cases require professional intervention to prevent long-term damage.
3. Are TMJ surgeries risky?
Modern TMJ surgeries are minimally invasive and have high success rates. Risks are low but include infection, nerve injury, or persistent discomfort if post-surgical care is neglected.
4. How long does TMJ recovery take?
Recovery varies by individual and treatment type. Non-surgical treatments may take 8–12 weeks, while surgical recovery can extend to several months.
5. Can stress cause TMJ disorders?
Yes. Chronic stress leads to jaw clenching and muscle tension, which are major contributors to TMJ pain and dysfunction. Relaxation and stress management are key elements of treatment.