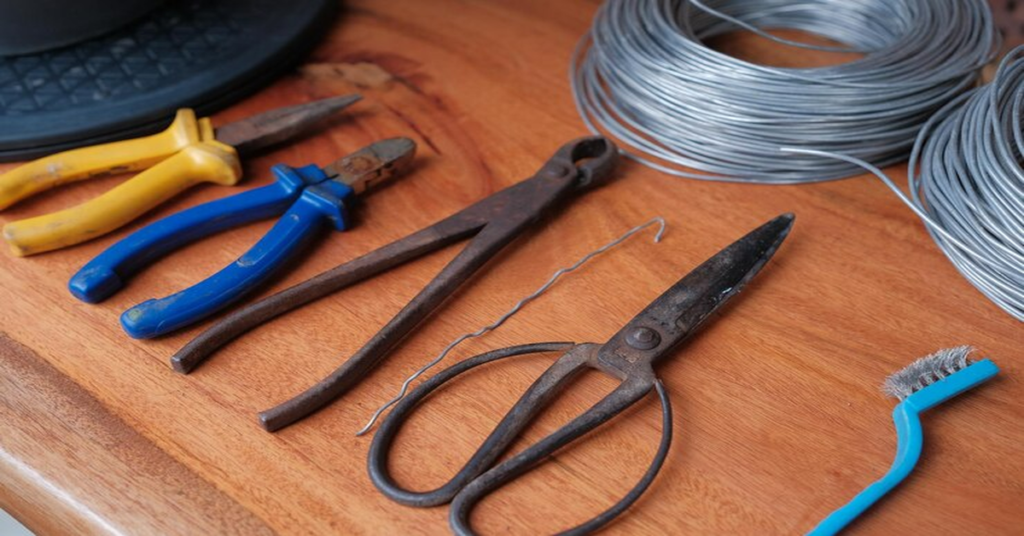
Wire cutters are essential hand tools used across various industries and in everyday household tasks. Designed to cut through different types of wire, these tools vary in shape, size, cutting ability, and purpose. Whether you’re an electrician, a DIY enthusiast, a jewelry maker, or an automotive technician, having the right wire cutter can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of your work.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about wire cutters—from their types and specific applications to how to choose the best one for your needs. Additionally, we’ll cover maintenance tips, safety precautions, and frequently asked questions to help you make informed decisions.
What is a Wire Cutter?
Definition and Basic Function
A wire cutter is a hand tool designed to cut wire and small metal objects. Typically made from hardened steel, wire cutters use leverage to apply a cutting force sufficient to snip through various materials.
Common Features
- Cutting blades
- Ergonomic handles
- Spring mechanisms
- Insulated grips (in electrical models)
Types of Wire Cutters
Diagonal Cutters
Also known as side cutters, diagonal cutters have angled cutting edges that make them ideal for snipping wires flush with a surface. They’re commonly used in electrical and electronics work.
End Cutters
These cutters have blades at the front of the tool and are used for cutting wire close to a surface, often in nail removal or twisting applications.
Lineman’s Pliers
Lineman’s pliers are multi-functional tools that can cut, twist, and grip wire. They are heavy-duty and often used by electricians.
Needle-Nose Pliers with Cutters
These are long, thin pliers with integrated cutting blades. Perfect for precision work in electronics or jewelry making.
Flush Cutters
These are designed to leave a clean, flat edge when cutting wire, making them ideal for electronic components and cable ties.
Cable Cutters
Built for heavy-duty applications, these cutters are used to cut thick cables such as coaxial, power, or communications cables.
Bolt Cutters
Though not traditionally labeled as wire cutters, bolt cutters are used to cut heavy-gauge wire, rods, and even chains.
Materials Wire Cutters Can Handle
Electrical Wire
Includes solid core and stranded wire commonly found in residential and commercial settings.
Steel Wire
Harder to cut; requires robust, high-leverage cutters or bolt cutters.
Aluminum Wire
Lighter and easier to cut, often used in overhead transmission lines.
Copper Wire
Frequently used in electronics and electrical systems, easily cut with standard wire cutters.
Jewelry Wire
Includes soft metals like silver, gold, or copper used in intricate designs. Requires precision tools like flush or needle-nose cutters.
Key Features to Consider When Buying
Cutting Capacity
Ensure the cutter matches the thickness and material of the wire you’ll be working with.
Handle Design
- Ergonomic: Reduces hand fatigue during prolonged use
- Non-slip grip: Enhances safety
- Insulated: Necessary for electrical applications
Build Quality
Look for tools made of high-carbon steel or chromium-vanadium alloy for durability and cutting strength.
Size and Portability
Choose based on application:
- Compact cutters for electronics and hobby use
- Large cutters for industrial settings
Brand and Warranty
Consider well-reviewed brands that offer warranties for reliability and customer support.
Top Wire Cutter Brands
- Klein Tools
- Knipex
- Irwin
- Channellock
- Hakko (for electronics)
- Craftsman
Applications of Wire Cutters
Electrical Work
- Cutting and stripping electrical wires
- Trimming wires during installations
Automotive Repair
- Removing battery cables
- Cutting wires in car audio installations
Jewelry Making
- Snipping fine wire
- Trimming ends on beadwork
DIY Projects
- Crafting
- Home repair
- Setting up home networks or AV systems
Industrial Use
- Machine assembly
- Heavy cable installations
- Factory maintenance
Maintenance Tips
Cleaning
- Wipe blades with a dry cloth after use
- Use alcohol or a mild cleaner for sticky residues
Sharpening
While not always necessary, you can:
- Use a fine metal file
- Send to a professional sharpening service
Lubrication
Apply a drop of machine oil to the pivot joint to ensure smooth operation.
Storage
- Keep in a dry place
- Use protective cases to avoid blade damage
Safety Guidelines
- Always wear safety goggles
- Do not exceed the cutter’s rated capacity
- Use insulated handles for electrical work
- Keep fingers away from cutting edges
- Ensure proper lighting in the workspace
Innovations in Wire Cutters
Ergonomic Advancements
Tools now feature improved grip materials, adjustable tension, and padded handles for enhanced comfort.
Electrical Safety Features
Insulated cutters with voltage ratings are now standard in professional electrical kits.
Smart Cutters
Some high-end models offer built-in sensors that detect wire thickness and automatically adjust cutting pressure.
Environmental Considerations
- Choose durable tools to reduce waste
- Opt for recyclable materials
- Consider multi-purpose tools to minimize consumption
Cost and Availability
Price Range
- Basic models: $5–$15
- Professional-grade: $25–$75
- Specialty cutters: $100 and up
Where to Buy
- Hardware stores
- Online marketplaces (Amazon, Home Depot, etc.)
- Specialty electrical or craft supply shops
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using the wrong cutter for the material
- Applying excessive force
- Neglecting safety precautions
- Failing to clean or oil the tool regularly
Conclusion
Wire cutters are indispensable tools that come in various forms, each tailored to specific materials and tasks. Understanding the types, functions, and maintenance requirements can greatly improve your work quality and safety. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a seasoned professional, investing in the right wire cutter will save time, reduce effort, and ensure precision.
From cutting delicate jewelry wire to snipping thick industrial cables, there’s a wire cutter designed for every job. By knowing what to look for and how to care for your tool, you can maximize its lifespan and effectiveness.
FAQs About Wire Cutters
1. Can wire cutters cut through steel?
Yes, but only if they are heavy-duty models designed for hardened steel. Standard cutters may not be effective.
2. Are wire cutters and wire strippers the same?
No. Wire cutters are for cutting, while wire strippers remove insulation from electrical wires without damaging the conductor.
3. How often should I replace my wire cutter?
With proper maintenance, a good wire cutter can last several years. Replace it when the blades dull or handles become damaged.
4. Can I sharpen wire cutters myself?
Yes, but only if you’re experienced. Otherwise, take them to a professional or replace them if they’re inexpensive.
5. What’s the safest wire cutter for electrical work?
Look for insulated wire cutters rated for electrical applications, ideally tested for up to 1,000 volts.
6. Can I use wire cutters for other materials like plastic?
Yes, they can cut soft plastic or zip ties, but doing so may dull the blades more quickly.